Data centre’s are the backbone of modern digital infrastructure, hosting the critical systems and applications that drive businesses, governments, and technology services worldwide. This blog explores the key components of data center infrastructure, providing insights into their types, power systems, cooling mechanisms, fire safety, networking, and other essential features. Additionally, we’ll discuss the critical aspects of downtime and availability from a business perspective.

What is a Data Center?
A data center is a facility that houses computing and networking equipment to store, process, and disseminate data. These centers ensure the uninterrupted operation of IT systems and services. Depending on their purpose and scale, data centers can be classified into several types:
- Enterprise Data Centers: Owned and operated by companies for internal use.
- Colocation Data Centers: Provide space, power, and cooling for servers owned by other businesses.
- Cloud Data Centers: Operated by cloud service providers like AWS, Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud.
- Edge Data Centers: Smaller facilities located closer to end-users to reduce latency.
Key Components of Data Center Infrastructure
1. Geographic Location and its Benefits:
Selecting the right location and ensuring proper construction are foundational to a data center’s success:
- Location Considerations: Proximity to users, availability of power and network connectivity, and low risk of natural disasters.
- Building Design: Must support heavy equipment, provide adequate space for expansion, and ensure structural integrity.
- Seismic and Weather Resistance: Designed to withstand local environmental conditions.
2. Raised Floor and Suspended Ceiling
Efficient layout designs enhance airflow and cable management:
- Raised Floors: Facilitate cooling by allowing cold air to circulate underneath and provide pathways for cabling.
- Suspended Ceilings: Used for air return paths and to house lighting and fire suppression systems.

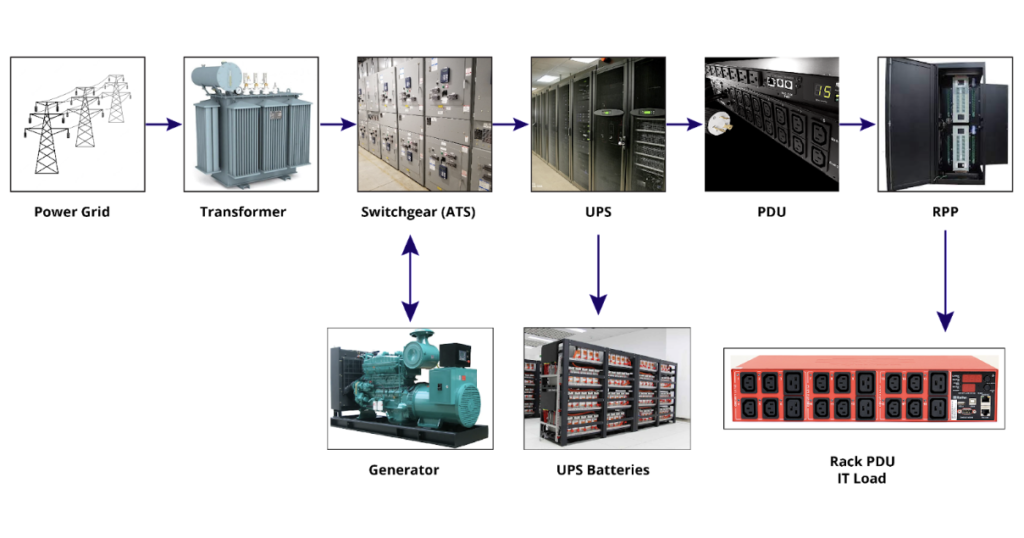
3. Power Infrastructure
Reliable power is the lifeblood of any data center. Key components include:
- Primary Power Supply: Typically sourced from the utility grid.
- Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS): Ensures continuous power during outages.
- Backup Generators: Provide long-term power backup.
- Power Distribution Units (PDUs): Distribute power efficiently to all equipment.
- Battery Systems: Used in UPS systems for immediate power needs.
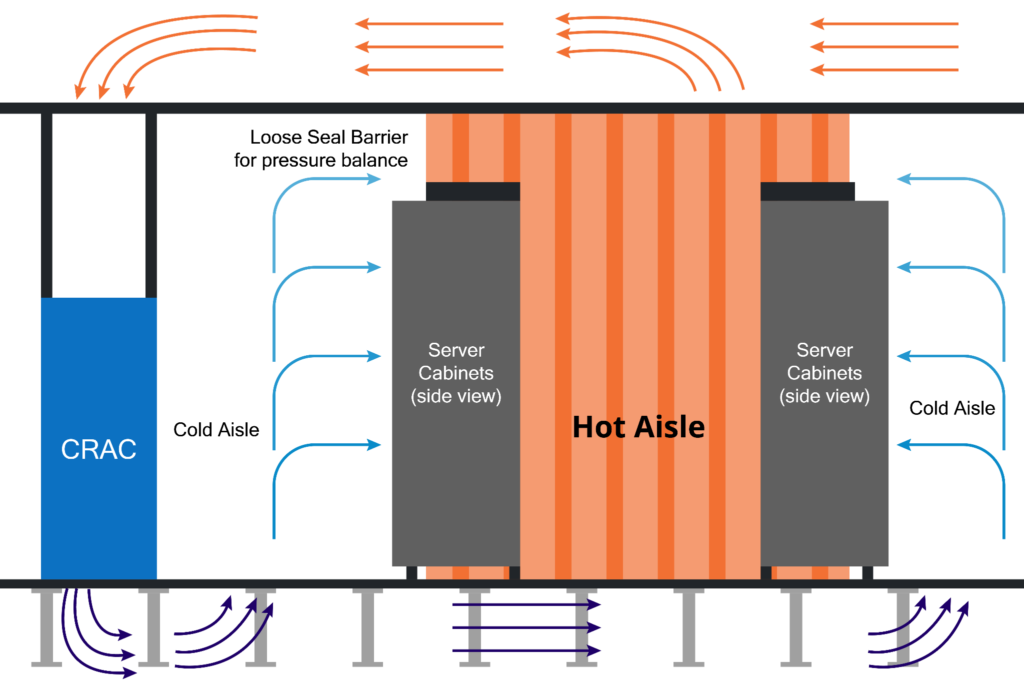
4. Cooling Systems
Efficient cooling is vital to maintain optimal operating temperatures for IT equipment. Common cooling solutions include:
- Computer Room Air Conditioners (CRAC): Specialized units for precise cooling.
- Chilled Water Systems: Use chilled water to dissipate heat.
- Direct Expansion (DX) Units: Use refrigerant-based cooling.
- Hot/Cold Aisle Containment: Separates hot and cold air to improve efficiency.
- Liquid Cooling: Direct cooling of servers using liquids, often for high-performance applications.
5. Lighting Systems
Proper lighting is essential for operational efficiency and safety:
- LED Lighting: Energy-efficient and long-lasting.
- Zoned Lighting: Reduces energy consumption by illuminating only occupied areas.
- Emergency Lighting: Ensures visibility during power outages or emergencies.

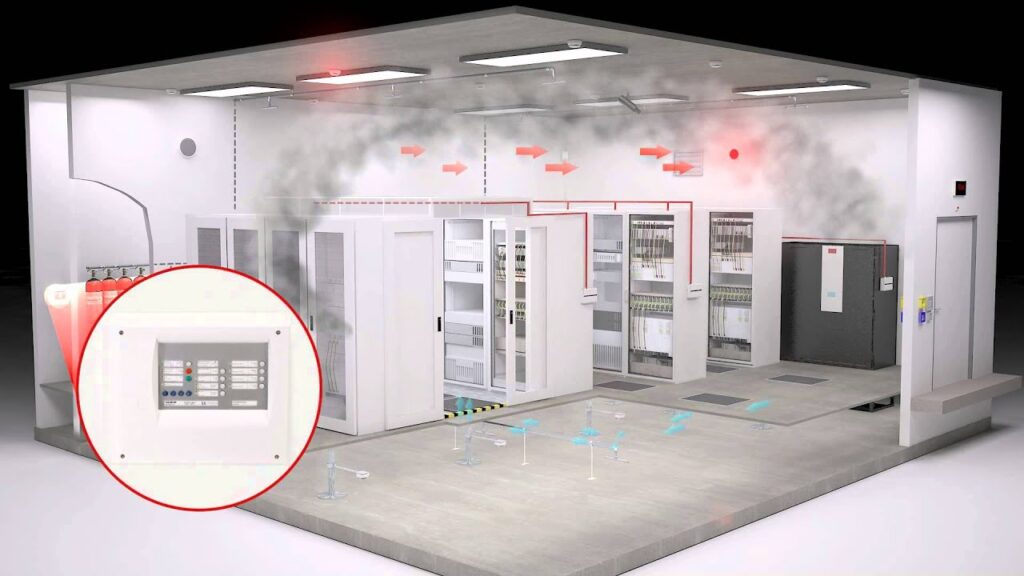
6. Fire Safety Systems
Data centers are equipped with advanced fire detection and suppression systems to protect critical infrastructure:
- Smoke Detectors: Detect early signs of fire.
- Fire Suppression Systems: Use gas-based systems like FM200 or inert gases to extinguish fires without damaging equipment.
- Firewalls and Compartmentalization: Physically separate areas to prevent fire spread.

7. Networking Infrastructure
Networking is the backbone of data center operations, enabling communication between servers, storage, and external networks:
- Switches and Routers: Facilitate data flow within and outside the data center.
- Structured Cabling: Ensures organized and efficient connectivity.
- Fiber Optics: High-speed connections for data transmission.
- Network Redundancy: Reduces downtime with multiple failover paths.

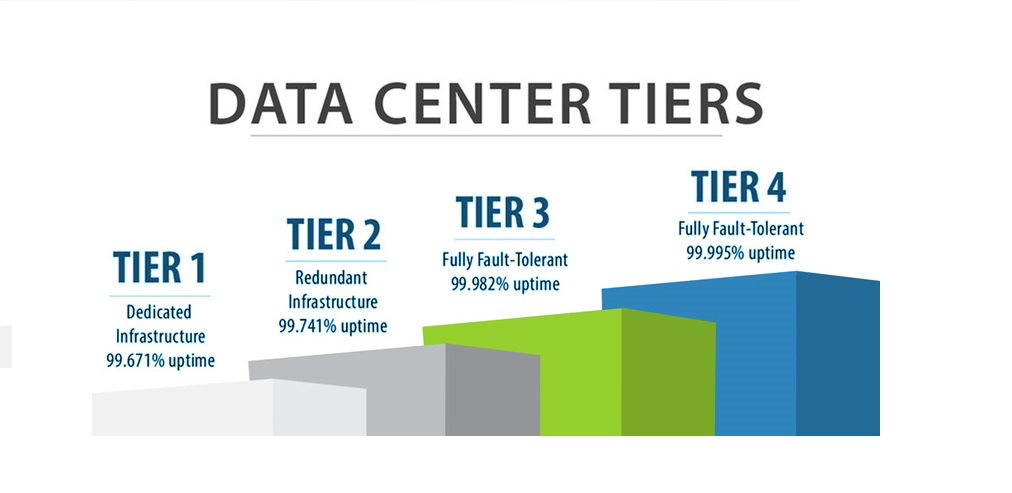
8. Downtime and Availability
From a business perspective, downtime and availability are critical factors influencing operational success:
- Downtime Impact: Even a few minutes of downtime can result in significant financial losses, damage to brand reputation, and disruption of critical services. Businesses relying on e-commerce, banking, or cloud services are particularly vulnerable.
- Availability Metrics: Measured using terms like uptime percentage, availability ensures that IT services remain operational. For example, achieving “five nines” (99.999%) availability translates to less than six minutes of downtime annually.
- Mitigation Strategies: Redundancy, failover systems, and proactive maintenance are essential to minimize downtime and ensure business continuity.
9. Environmental Monitoring Systems (EMS)
Monitoring environmental conditions ensures optimal performance and prevents equipment failures:
- Temperature and Humidity Sensors: Maintain ideal operating conditions.
- Leak Detection Systems: Identify water leaks early to prevent damage.
- Air Quality Monitors: Ensure clean air circulation.
10. Data Center Infrastructure Management (DCIM)
DCIM tools provide a comprehensive view of data center operations:
- Real-Time Monitoring: Tracks power usage, temperature, and system health.
- Capacity Planning: Helps optimize space, power, and cooling resources.
- Predictive Analytics: Identifies potential issues before they escalate.

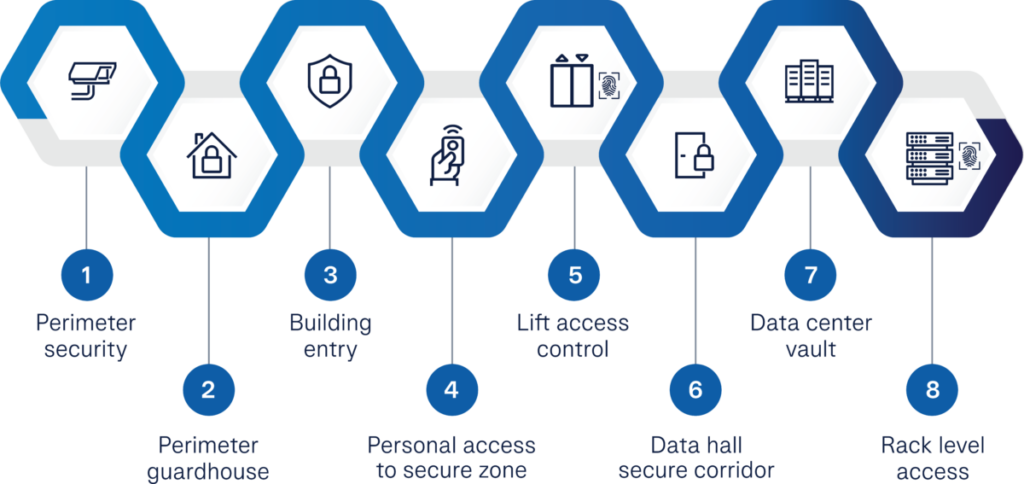
11. Security Systems
Ensuring the physical and digital security of a data center is critical:
- Access Control Systems: Restrict entry to authorized personnel.
- Surveillance Cameras: Monitor activities in and around the facility.
- Cybersecurity Measures: Protect against data breaches and cyber threats.
12. Other Essential Features
- Scalability: Modular designs to accommodate growth.
- Energy Efficiency: Use of renewable energy sources and energy-efficient equipment to reduce carbon footprints.
- Redundancy: Ensures high availability through N+1 or 2N configurations.
The Importance of a Well-Designed Data Center
A robust data center infrastructure ensures:
- High Availability: Minimized downtime for critical services.
- Scalability: Ability to grow with business needs.
- Energy Efficiency: Reduced operational costs and environmental impact.
- Security: Protection of sensitive data and systems.
Conclusion
Data centers are complex ecosystems requiring meticulous planning and execution to ensure reliability, efficiency, and security. By understanding the key components and their roles, businesses can make informed decisions about their IT infrastructure. Whether you’re building an enterprise data centre or leveraging cloud solutions, prioritizing power, cooling, fire safety, networking, and availability will ensure long-term success.
References :
- Role of VAV in Commercial Buildings: How It Works and Why It Matters
- Scope of Cold Rooms in the Indian Economy: Growth, Applications, and Infrastructure Demand
- HVAC Filter Cost vs Energy Savings: Dirty Filters Increase SFC
- Motor Selection and Energy Savings in HVACR Systems
- Energy-Saving Opportunities in AHUs


