Why Heat Pumps Are Gaining Popularity
Have you ever wondered how to keep your home comfortable year-round while cutting down on energy bills? Heat pumps are quickly becoming the go-to solution for homeowners. With rising electricity costs, evolving climate conditions, and generous government incentives, switching to a heat pump is no longer just an option—it’s a smart move.

Table of Contents
- What Is a Heat Pump?
- Heat Pumps vs. Air Conditioners: Key Differences
- How Heat Pumps Work & Their Types
- How to Choose the Right Heat Pump
- Key Factors to Consider
- Real-World Scenario
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Conclusion
1. What Is a Heat Pump?
A heat pump is a highly efficient HVAC system that transfers heat instead of generating it. Unlike traditional furnaces that burn fuel, heat pumps use refrigerant cycles to extract heat from the air, water, or ground to provide both heating and cooling. This dual functionality makes them a cost-effective and environmentally friendly alternative to conventional heating and cooling systems.
2. Heat Pumps vs. Air Conditioners: Key Differences
Many homeowners confuse heat pumps with air conditioners. While both systems rely on similar cooling mechanisms, heat pumps offer an additional advantage: they provide heating as well.
| Feature | Heat Pump | Air Conditioner |
|---|---|---|
| Cooling Capability | Yes | Yes |
| Heating Capability | Yes | No |
| Energy Efficiency | High (uses ambient heat) | Moderate |
| Best For | Year-round comfort | Summer cooling only |
If you’re looking for a solution that works throughout the year without the need for a separate heating system, a heat pump is the way to go.
3. How Heat Pumps Work & Their Types
Think of a heat pump as a smart heat transporter—it moves heat from one place to another rather than generating it. Depending on the type of system, it extracts heat from different sources:
- Air-Source Heat Pumps (ASHPs): These are the most common type, extracting heat from outdoor air. They work best in moderate climates, but advanced models can function efficiently even in colder regions.
- Water-Source Heat Pumps (WSHPs): These use water as a heat exchange medium. They offer excellent efficiency but require access to a water loop or a nearby body of water.
- Ground-Source Heat Pumps (GSHPs or Geothermal): These harness stable underground temperatures, providing unmatched efficiency and year-round performance. While initial installation costs are higher, long-term savings are substantial.
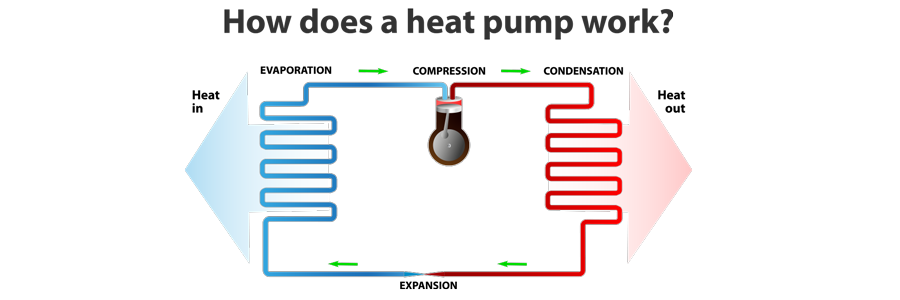
Choosing the right type depends on your location, budget, and energy efficiency goals.
4. How to Choose the Right Heat Pump
Selecting the perfect heat pump isn’t just about picking a brand—it’s about understanding what fits your home’s needs. Let’s break down the key factors.
Key Factors to Consider
1. Understanding Your Home’s Heat Load
The heat load refers to the energy required to maintain a comfortable indoor temperature. A professional HVAC technician can perform a heat load calculation based on factors such as:
- Home size
- Insulation levels
- Climate conditions
Choosing a unit that matches your heat load ensures optimal efficiency and comfort.
2. Climate Matters!
- Cold Climates: If you live in areas like Canada or the northern U.S., opt for cold-climate heat pumps with high Heating Seasonal Performance Factor (HSPF) ratings.
- Mild Climates: Standard air-source heat pumps work well in moderate temperatures, offering an energy-efficient alternative to traditional HVAC systems.
3. Efficiency Ratings: COP, HSPF & SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio)
| Heat Pump Type | COP | HSPF | SEER |
|---|---|---|---|
| Air-Source Heat Pump | 2.5 – 4.0 | 8 – 12 | 14 – 22 |
| Water-Source Heat Pump | 3.0 – 5.5 | 10 – 14 | 16 – 24 |
| Ground-Source (Geothermal) | 4.0 – 6.0 | 12 – 16 | 20 – 30 |

4. Warranty & After-Sales Support
Opt for models with longer warranties on compressors and key components. Leading brands like Trane, Carrier, and Mitsubishi Electric offer extended warranties and industry-leading reliability.
5. Smart Features & IoT Integration
Wouldn’t it be great to control your heat pump remotely? Many modern models come with Wi-Fi connectivity, smart thermostats, and mobile app control, allowing you to fine-tune your home’s temperature anytime, anywhere.

6. Government Rebates & Incentives
Many governments offer financial incentives for energy-efficient upgrades.
Popular programs include:
- U.S. Inflation Reduction Act (IRA)
- Canada’s Greener Homes Grant
Check energy.gov or nrcan.gc.ca to see what rebates are available in your area.
5. Real-World Scenario: Finding the Perfect Heat Pump
Let’s say you live in Chicago, where winters are freezing, and summers are warm. A standard heat pump might struggle in subzero temperatures. In this case, a cold-climate ASHP with an HSPF of 10+ would be the ideal choice.
On the other hand, if you own a commercial building near a lake, a water-source heat pump could provide ultra-high efficiency while using natural water bodies for heat exchange.
6. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Are heat pumps worth it for cold climates?
A: Yes! Look for Cold-Climate Heat Pumps (CCHPs) with an HSPF of 10+ and a backup electric coil.
Q: What size heat pump do I need for my home?
A: A 1,500 sq. ft. home typically needs a 2.5-ton heat pump, but a professional should conduct a Manual J load calculation.
Q: Do heat pumps work during power outages?
A: No, they rely on electricity. Consider a battery backup or hybrid system if power outages are frequent.
7. Conclusion: The Future of Home Heating & Cooling
The right heat pump can slash your energy bills, reduce your carbon footprint, and provide all-season comfort. By considering factors like climate, efficiency ratings, and rebate opportunities, you can make an informed decision that benefits both your home and the planet.
Take control of your energy bills TODAY! Get a personalized heat pump consultation and find the best rebates available in your area.


